Bacteria can cause different types of skin infections. Three common skin infections treatment that you may encounter are: (1) cellulitis, (2) folliculitis, and (3) impetigo. Keep in mind that skin infections vary in presentation and treatment. Therefore, it is important to talk to your doctor to obtain an appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is an infection that involves the outer layers of the skin. It is commonly caused by bacteria known as beta-haemolytic streptococcus or Staphylococcus aureus. You may experience pain, swelling, tenderness, warmth, and redness in the infected area. If you have a severe case of cellulitis, you may experience fever, tiredness, and a lowering of blood pressure. If left untreated, pus may form, and cells may die in the infected skin area. Cellulitis can involve any part of the body but most often affects the leg. It typically results from an injury to the skin, such as scratches or animal bites—these allow bacteria to enter the body and cause an infection.
Oral antibiotics are used to treat mild cellulitis; more severe cases must be treated with intravenous antibiotics in a hospital. Swelling can be lessened by elevating the affected area, such as the legs or arms. To stop cellulitis from occurring again, it is important to keep applying lotion to the skin and to maintain good skin cleanliness.
Folliculitis
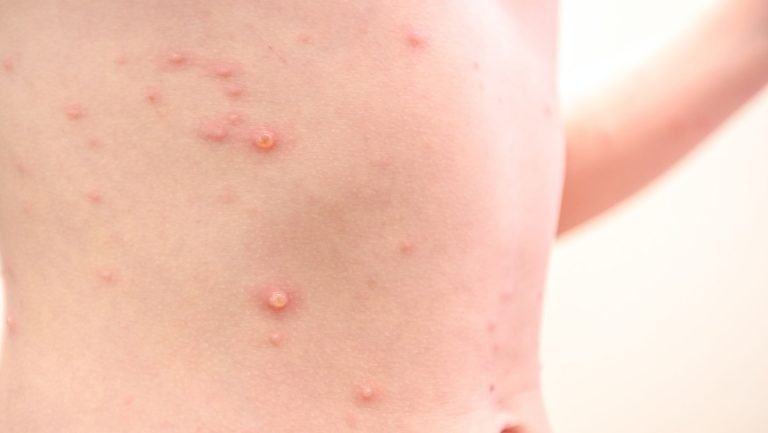
Folliculitis is a general term used to describe an infection of the hair follicles, resulting in red pimples. You may experience redness, tenderness, or swelling of the affected area. It also can spread to the deeper parts of the hair follicles and pus can form Folliculitis can be seen on any part of the body with hair, such as the face, scalp, thighs, underarms, and groin area. This includes areas that are bearded or shaved.
Mild folliculitis can be treated with topical antibiotics. More severe infections may require a surgical cut and drainage of the affected area. After drainage, it is important to clean the area with antibacterial soap; then you should apply the antibiotic ointment to the affected area of the skin. If needed, your doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics. Keep in mind that your doctor may recommend monthly treatments if you have folliculitis that occurs repeatedly.
Impetigo
Impetigo is a contagious skin infection. Although this infection may occur in adults, it is most often seen in children aged 2 to 5 years and is usually spread through direct contact with another person who has the infection. You may experience tenderness, itching, sores, or blisters that can rupture and form honey-coloured crusts. It can affect different parts of the body such as the face, arms, or legs.
Impetigo can be treated with a topical ointment or oral antibiotic. To prevent the spread of the infection to other parts of the body, avoid scratching the blisters or sores. Because impetigo is commonly seen in children, it may be helpful to cut the fingernails and cover the affected areas of the body with bandages or gauze. It also is important to prevent the spread of infection to other individuals in close contact by not sharing things such as blankets, linens, toys, or clothing.
General Management of Skin Infections
With antibiotic treatment, signs and symptoms of skin infections begin to improve after approximately 2 to 3 days. If your skin infection does not improve or gets worse (especially if you develop a fever or the infection spreads), notify your doctor right away. If you are prescribed topical or oral antibiotics, be sure to finish the full course of antibiotics unless otherwise directed. Keep in mind that the length of treatment will differ depending on the type and severity of the infection. Lastly, as is true among all skin infections, you should keep the affected area or wound clean with good skin hygiene.
Other than these obvious factors, many times even in the most well fed and aware persons , nutritional factors can play a big role in causing recurrence of such infections by impacting the immunity.
Other than taking the best treatment, it is most important to maintain our immune status in balance using principles of time tested science of traditional indian systems of medicine. The management of sudden excess intake of high carb. foods and high sugar foods should be avoided.
The importance of skin microbial balance is extremely complex but is being studies very vigorously as a new dimension in management of skin infections